Stroke
- Overview
- Signs and Symptoms
- Causes and Risk Factors
- Diagnosis and Testing
- Treatment
- Possible Complications
- Living with
All body cells receive constant supply of oxygen and nourishment through the blood supply. Since brain and heart are the most important organs, any interruption in blood supply can result in severe health effects or even death.
A stroke is caused by interruption in supply of oxygen-rich blood to a part of the brain due to a blockage or leakage. When part of the brain does not receive the oxygen or blood, it is not being properly nourished and the cells begin to die.
Some strokes are caused by sudden bleeding that causes damage to brain cells. The part of the brain affected determine a person's symptoms.
A stroke is a life-threatening condition that requires emergency medical attention. Every minute matters.
It is among the top three causes of death globally and the major cause of long-term disability. Those who experience a stroke are at risk for long-term disability, brain damage and even death.
There are two main types of stroke:
Ischemic stroke – occurs when the blood supply is stopped or interrupted due to a blockage caused by a blood clot or fatty material in the artery supplying blood to the brain. This is the most common type of stroke.

Hemorrhagic stroke – In this type, an artery supplying blood to brain breaks open or leaks the blood in the brain which starts to accumulate and puts pressure on the brain.

The signs of a stroke are most noticeable to those around you because there are changes that occur that are generally very visible. Signs and symptoms develop very fast and include:
- Difficulty walking due to loss of balance, dizziness or loss of coordination
- Sudden feeling of numbness or paralysis affects a limb or a part of the face
- A headache that is severe and sudden
- Sudden difficulty in understanding or speaking, slurring words and confusion
- Difficulty seeing things and this may affect both eyes in some cases
Remember S –T – R and ask patient to:
- S - Smile
- T - Talk
- R - Raise both arms
The symptoms usually affect one side of the body. For example, if the right arm is numb, usually it is noticed that when the person tries to smile, the right side of the mouth droops.
The blockage of blood flow or blood building up on a part of the brain cause a stroke. There are many different risk factors that increase the chances of experiencing a stroke at some point in life. Many of these are things you can work toward changing to reduce your risk.
Risk factors include:
- High blood pressure - hypertension (Can damage the blood vessels which can cause Hemorrhagic stroke)
- High cholesterol (Can form plaque or fatty material in the blood vessels which can block the blood vessels resulting in Ischemic stroke)
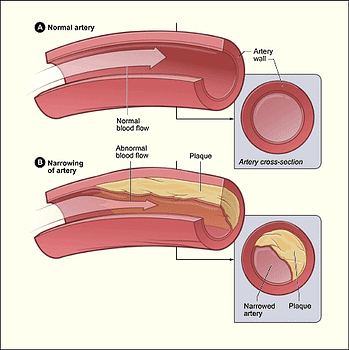
- Heart disease
- Person’s who have previous stroke or transient ischemic attack (mini-stroke)
- Diabetes
- Obesity and being overweight
- Family history of stroke
- Not exercising regularly
- Smoking cigarettes
- Excessive alcohol use
- Being over age 55
- Being male (stroke is more common in men)
Strokes are diagnosed in an emergency environment so the process moves very quickly and there are often several people performing multiple tests at once. The doctor will perform a detailed examination to look at your blood pressure, test your strength, listen to your heart and look into your eyes. Throughout this time, he or she will also be asking about the medications and medical history.
Blood testing is done to look at the blood sugar, to look for signs of infection, to see how quickly the patient blood clots and to look at the balance of chemicals in the blood. These tests help to determine the type of stroke (Ischemic or Hemorrhagic) and how the stroke can be treated and cared for.
A CT scan looks at the brain and gives the doctor a detailed view. They may use a special dye to further enhance the images. They are looking for many things, such as strokes, hemorrhage and tumors. An MRI may also be done to assess the damage of the stroke.
To look at the major arteries in and near the brain, a carotid ultrasound, magnetic resonance venography, cerebral angiogram or magnetic resonance angiography may be done. This gives the doctor a good view to look for issues like blockages or blood vessel damage.
If the doctor suspects blood clots in the heart, an echocardiogram may be done. This helps to find the source of any clots that may have traveled to the brain and caused the stroke.
A stroke is a medical emergency that requires emergency medical attention.
Patient’s survival and brain damage minimization largely depends on bringing the patient to the hospital in the shortest possible time.
The treatment used depends on the type of stroke a person has.
Treatment for an ischemic stroke is as follows:
Emergency medications are very commonly used and they used to prevent clots or bust them up. Aspirin works to prevent more clots while a medication called tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) works to break up clots that have already formed. tPA may be delivered straight to the brain if the situation calls for it. If required, the doctor may also do surgery to remove the clot from the brain.
If there are large plaques in the carotid artery (main artery in the neck that goes to the brain) your doctor may perform a carotid endarterectomy. This requires opening the artery and removing any blockages. To keep an artery open after working on it, your doctor may place stents.
With a hemorrhagic stroke, many medications are often given quickly to lower pressure in the brain, prevent further bleeding, lower the blood pressure and prevent seizures. If there is a large bleed on the brain, the blood may need to be removed through a procedure. The blood vessel responsible for the bleeding needs to be repaired quickly and there are three main surgical procedures to do this:
- Coiling: This works to stop an aneurysm which strengthens the blood vessel
- Surgical clipping: This clips off the weak part of the blood vessel
- Surgical AVM removal: If the bad area of the vessel is small, the doctor can remove it
When someone has a stroke, there is always a risk for complications that everyone should be aware of and these may include:
- Loss of muscle movement or paralysis
- Problems with thinking or memory loss
- Strange sensations, such as numbness or pain
- Trouble with swallowing or talking
- Difficulty controlling emotions
- Behavioral changes
- Difficulties with self-care
After a stroke, the patient may require help, depending on the effects of stroke. It is also important to look at your total health and do what you can to improve it. The following are important after a stroke:
- Keep blood pressure under control
- Exercise regularly
- Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet (reduce salt in-take and cholesterol rich diet)
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Keep diabetes under control
- Avoid alcohol

